Text
When creating a web page, you add tags (known as markup) to the contents of the page. These tags provide extra meaning and allow browsers to show users the appropriate structure for the page.
- Structural markup: the elements that you can use to describe both headings and paragraphs
- Semantic markup: which provides extra information; such as where emphasis is placed in a sentence, that something you have written is a quotation (and who said it), the meaning of acronyms, and so on
- Headings
<h1></h1>to<h6></h6>theh1is the big one and theh6is the smalist one - Paragraphs
<p></p>To create Paragraph we use theptag - Bold & Italic to bold a text use the
<b>tag and to make it italic use<i>tag - Superscript & Subscript The
<sup>element is usedto contain characters thatshould be superscript such as the suffixes of dates The<sub>element is used to contain characters that should be subscript. It is commonly used with foot notes or chemical formulas such as H2O. - White Space one space will shown in browser
- Line Breaks & Horizontal Rules to go down one line use
<br />to add ahorizontal rules<hr/> - Strong & Emphasis The use of the
<strong>element indicates that its content has strong importance. The<em>element indicates emphasis that subtly changes the meaning of a sentence - Quotations The
<blockquote>element is used for longer quotes that take up an entire paragraph. Note how the<p>element is still used inside the<blockquote>element. The<q>element is used for shorter quotes that sit within a paragraph. Browsers are supposed to put quotes around the<q>element, however Internet Explorer does not — therefore many people avoid using the<q>element. - Abbreviations & Acronyms If you use an abbreviation or
an acronym, then the
<abbr>element can be used. A title attribute on the opening tag is used to specify the full term. - Citations & Definitions When you are referencing a
piece of work such as a book,
film or research paper, the
<cite>element can be used to indicate where the citation is from. The<dfn>element is used to indicate the defining instance of a new term. - Author Details The
<address>element has quite a specific use: to contain contact details for the author of the page. - Changes to Content The
<ins>element can be used to show content that has been inserted into a document, while the<del>element can show text that has been deleted from it. The<s>element indicates something that is no longer accurate or relevant (but that should not be deleted).
Example
Copy the Code and add it to new
file.htmlas we learn in last episod and see every thing about text .
<html>
<head>
<title>Text</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The Story in the Book</h1>
<h2>Chapter 1</h2>
<p>Molly had been staring out of her window for about
an hour now. On her desk, lying between the copies
of <i>Nature</i>, <i>New Scientist</i>, and all
the other scientific journals her work had
appeared in, was a well thumbed copy of <cite>On The Road</cite>. It had been Molly’s favorite book
since college, and the longer she spent in these
four walls the more she felt she needed to be
free.</p>
<p>She had spent the last ten years in this room,
sitting under a poster with an Oscar Wilde quote
proclaiming that <q>Work is the refuge of
people who have nothing better to do</q>. Although
many considered her pioneering work, unraveling
the secrets of the llama <abbr title="Deoxyribonucleic acid">DNA</abbr>, to be an
outstanding achievement, Molly <em>did</em> think
she had something better to do.</p>
</body>
</html>
Summary TEXT
- HTML elements are used t XX o describe the structure of the page (e.g. headings, subheadings, paragraphs).
- They also provide semantic information (e.g. where emphasis should be placed, the definition of any acronyms used, when given text is a quotation).
Introducing CSS
- What CSS does
- How CSS works
- Rules, properties, and values
CSS allows you to create rules that specify how the content of
an element should appear. For example, you can specify that
the background of the page is cream, all paragraphs should
appear in gray using the Arial typeface, or that all level one
headings should be in a blue, italic, Times typeface.
Understanding CSS:
Thinking Inside the Box
The key to understanding how CSS works is to imagine that there is an invisible box around every HTML element.
BLOCK & INLINE ELEMENTS
Block level elements look like they start on a new line. Examples include the
<h1>-<h6>, <p> and <div>elements. Inline elements flow within the text and do not start on a new line. Examples include<b>, <i>,<img>, <em> and <span>.
CSS allows you to create rules that control the way that each individual box (and the contents of that box) is presented.
Example Styles | Boxes | Text | Specific | | ———– | ———– | ———– | | Width and height Borders (color, width, and style) Background color and images Position in the browser window | Typeface Size ColorItalics, bold, uppercase,lowercase, small-caps | There are also specific ways in which you can style certain elements such as lists, tables, and forms. |
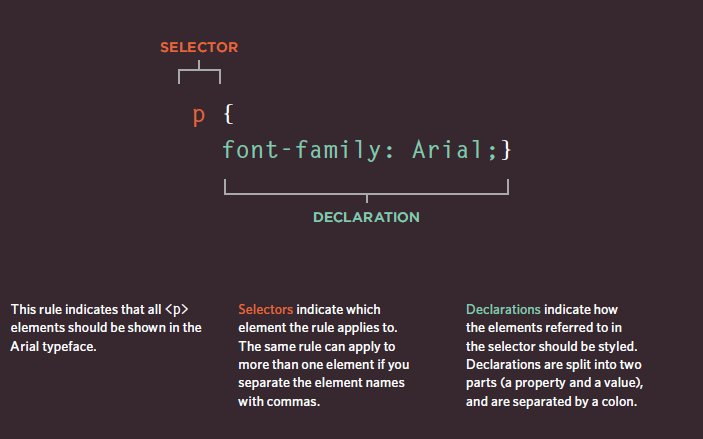
CSS Associates Style rules with HTML elements
CSS works by associating rules with HTML elements. These rules govern how the content of specified elements should be displayed. A CSS rule contains two parts: a s
elector and a declaration.
There are three way to add css to Html
- Inline inside the element
<h1 style="color:blue;"> </h1> - External adding dierctory
style.cssand connected it using<link src=""> - Internal inside HTML page between
<style></style>
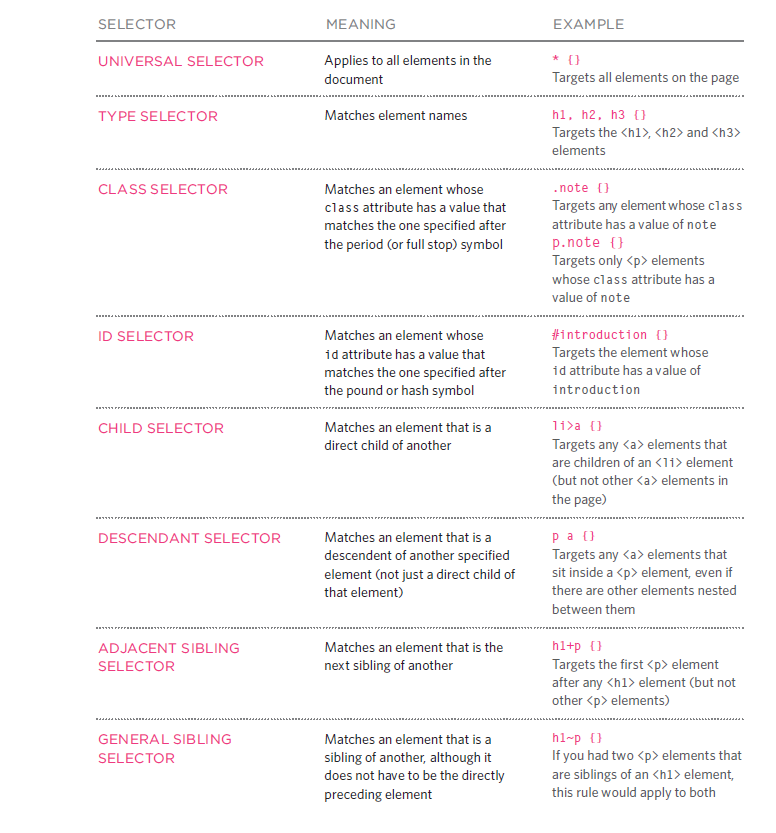
Selectors
Summary
CSS treats each HTML e XX lement as if it appears inside its own box and uses rules to indicate how that element should look. Rules are made up of selectors (that specify the elements the rule applies to) and declarations (that indicate what these elements should look like). Different types of selectors allow you to target your rules at different elements. Declarations are made up of two parts: the properties of the element that you want to change, and the values of those properties. For example, the font-family property sets the choice of font, and the value arial specifies Arial as the preferred typeface. CSS rules usually appear in a separate document, although they may appear within an HTML page.
Questions
-
What is CSS?
-
Cite different types of CSS ?
-
How to use CSS selector?
JavaScript
Tody we are going to learn about JavaScript it also called JS
JavaScript can be used in browsers to make a website more interactive, intresting,and user friendly JavaScript is a programing language.
First thing first :
you will need a basic knowldge to know how to build webpages using HTML and CSS
After that :
You know about :
- Basic progroaming consepts .
- The language itself.
- How to applied what you learn .
If you are writing an Js code inside html page it should be in <script></script> Tag
You can use the JS to :
- Access content
- Modify Content
- Program rule
- React
Befor looking at java Scripts lets calairfy some Html & Css Terms
#### Before you learn how to read and write in js languge itself you need to become familiar with some key

How to write a Script :
- To write a Script you need at first
- Set your goal
- list the task
- complete the task in order to achive it
- Start with a big picture
After setting the goal
- Define it
- Design the Script for it
- Code each steps
Expressinon
An expressinon evaluate into result in a single value.
- There are two type of expressinon
- Assign value to variable
var animal="Cow" - Two or more value to return one value
var area =7*5
- Assign value to variable
Operators
Expression relay on somthing called operators
- the type of it :
- Assigment operators
color = "red"- Arithmatic operators
area = 3 * 2- String operators
name = "mohammad" + "Azzam"- Comparison operators
b = 3 > 5the value True or False- Logical operators
ax = (5>3) && (3 <5 )it’s return false if one of them false and true if both of them are true
DECISIONS
Using the results ofevaluations, you candecide which path your script should go down.
- using if statment :
if()statment evaluate or check a condition if true do something else do another thing.- if else statment :
if(){// code} else if (){ //code} else {}LOOPS
There are also many occasions where you will want to perform the same set of steps repeatedly.
for()
SUMMARY
- Conditional statements allow your code to make decisions about what to do next.
- Comparison operators
(===, ! ==, ==, ! =, <, >, <=, =>)are used to compare two operands. - Logical operators allow you to combine more than one set of comparison operators.
- if … else statements allow you to run one set of code if a condition is true, and another if it is false.

